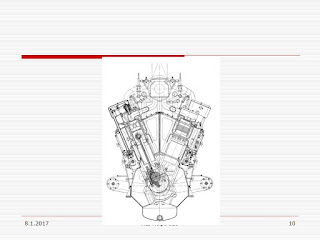
GEMİ MAKİNELERİ II Baş Müh. 8.1.2017 2 Diesel Basics Top Dead Center (TDC) -- highest position of piston in cylinder Bottom Dead Center (BDC) -- lowest position of piston in cylinder Stroke (S) -- distance between TDC and BDC Bore (B) -- diameter of cylinder Displacement (D) -- swept volume of all cylinders in engine Compression Ratio (CR) -- ratio of cylinder volume at BDC to cylinder volume at TDC Piston Speed (Vp) -- average speed of piston during stroke 8.1.2017 3 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing 8.1.2017 4 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing 8.1.2017 5 Diesel Rotational Speeds Slow Speed 100 - 200 rpm 5,000 to over 40,000 bhp Generally two-stroke cycle, large bore Commercial applications only Medium Speed 400 - 1,200 rpm 1,000 to over 40,000 bhp Generally four-stroke cycle Naval and commercial applications High Speed 1,200 - 2,000 rpm Less than 100 to 4,000 bhp Four-stroke cycle Naval and commercial applications 8.1.2017 6 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing 8.1.2017 7 Diesel Cylinder Arrangements In-line Cylinders are arranged in a line Generally for eight or less cylinders Require less beam, but more length, than Vee engines Vee The other most common arrangement (besides in-line) Cylinders are in two banks, angled to form a “V” Standard for engines with more than eight cylinders Require less length, but more beam, than in-line engines W and X More compact, but harder to access, and not commonly used Opposed pistons Two-stroke engines with two pistons sharing a common cylinder Usually in-line with one or two crankshafts 8.1.2017 8 8.1.2017 9 8.1.2017 10 8.1.2017 11 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing 8.1.2017 12 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing 8.1.2017 13 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing 8.1.2017 14 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing
Bilgi bloğu, Denizcilik bilgi arşivi,teknik terimler,teknik kavramlar,teknik açıklamalar ,bilgi kaynağı, ödev, denizcilik dökümanları,nedir? sorusunun cevabı
10 Mart 2017 Cuma
Ship Diesel Basics
GEMİ MAKİNELERİ II Baş Müh. 8.1.2017 2 Diesel Basics Top Dead Center (TDC) -- highest position of piston in cylinder Bottom Dead Center (BDC) -- lowest position of piston in cylinder Stroke (S) -- distance between TDC and BDC Bore (B) -- diameter of cylinder Displacement (D) -- swept volume of all cylinders in engine Compression Ratio (CR) -- ratio of cylinder volume at BDC to cylinder volume at TDC Piston Speed (Vp) -- average speed of piston during stroke 8.1.2017 3 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing 8.1.2017 4 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing 8.1.2017 5 Diesel Rotational Speeds Slow Speed 100 - 200 rpm 5,000 to over 40,000 bhp Generally two-stroke cycle, large bore Commercial applications only Medium Speed 400 - 1,200 rpm 1,000 to over 40,000 bhp Generally four-stroke cycle Naval and commercial applications High Speed 1,200 - 2,000 rpm Less than 100 to 4,000 bhp Four-stroke cycle Naval and commercial applications 8.1.2017 6 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing 8.1.2017 7 Diesel Cylinder Arrangements In-line Cylinders are arranged in a line Generally for eight or less cylinders Require less beam, but more length, than Vee engines Vee The other most common arrangement (besides in-line) Cylinders are in two banks, angled to form a “V” Standard for engines with more than eight cylinders Require less length, but more beam, than in-line engines W and X More compact, but harder to access, and not commonly used Opposed pistons Two-stroke engines with two pistons sharing a common cylinder Usually in-line with one or two crankshafts 8.1.2017 8 8.1.2017 9 8.1.2017 10 8.1.2017 11 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing 8.1.2017 12 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing 8.1.2017 13 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing 8.1.2017 14 Types of Marine Diesel Engines Cycle Two-stroke Four-stroke Speed of Rotation Slow speed Medium speed High speed Cylinder Arrangement Inline Vee Opposed piston W or X Cooling Method Liquid Air Air Supply Method Naturally aspirated Scavenged Supercharged (Turbocharged) Starting Means High pressure air Electric motor Direction of Rotation Reversing Non-reversing
Kaydol:
Kayıt Yorumları (Atom)












Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder